|
RADRESPONSE™ |
|
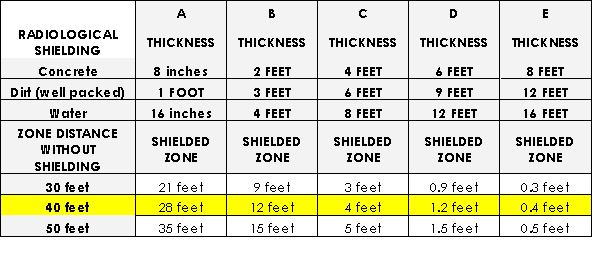
Learning Scenario #9 NRC Incident Report For this scenario, assume that at least one of the sources is exposed. Your hazmat team has been dispatched to the scene at 11:40 for an auto accident involving radioactive materials. State Highway 44 is a two-lane highway and both lanes are blocked. When you approach the scene, your radiation detectors alarm at 0.1 mR/hr at 178 feet from the scene. Other responders are already at the vehicle. You are advised that the driver is deceased and there is no danger of fire, and you instruct everyone to move back 178 feet. Based on responder observations, and visual assessment with binoculars, you determine that the radioactive packages are located on the outer edge of the shoulder of the westbound lane. Sheriffs tell you that they need to clear the road as soon as possible because Highway 44 is the main east - west travel route between Encinal and Corpus Christi. 1. Based on an exposure rate of 0.1 mR/hr at a distance of 178 feet, what is the distance of the NCRP exclusion zone of 2 mR/hr? You can find your answer by using the following formula: Exposure Rate X Distance2 Zone Distance = √ —————————————————————- NCRP Guideline 0.1 mR/hr X (178 feet)2 Zone Distance = √ —————————————————————- 2 mR/hr A. 360 feet B. 90 feet C. 40 feet D. 20 feet 2. Each shoulder of Highway 44 is twelve feet in width. Using the table below, how much shielding would you need to decrease the NCRP Exclusion zone from 40 feet to 12 feet to allow the travel lanes of the roadway to be opened? 3. Based on the exposure rate of 0.1 mR/hr at 178 feet from the source, what would the exposure rate be at 2 feet from the source where the entry team will need to work to place the shielding? Use the following formula: Detector Exposure Rate X (Detector Distance)2 Entry Exposure Rate = ———————————————————————- (Entry Activity Distance)2 0.1 mR/hr X (178 feet)2 Entry Exposure Rate = —————————————————————- (2 feet)2 A. 793 mR/hr B. 8 R/hr C. 1.6 R/hr D. 1584 mR/hr 4. Based on the Entry Exposure Rate at 2 foot (Answer #3) and the EPA Single Incident Dose Limit for “Any Activity” of 5 rem, how much time would the responders have to place the shielding? Use the following formula: Entry Time = Dose Limit ÷ Entry Exposure Rate Entry Time = 5 Rem ÷ Answer #3 (in R/hr) B. 23 Seconds C. 14 minutes 5. Ir-192 emits beta radiation (average energy greater than 10% probability: 161 KeV, 208 KeV), and gamma radiation (greater than 10% probability: 295 KeV, 308 KeV, 316 KeV, 468 KeV), and has a half life of 74 days. Sc-46 emits beta radiation (average energy greater than 10% probability: 112 KeV), and gamma radiation (greater than 10% probability: 889 KeV, 1.12 MeV), and has a half life of 83 days. Sb-124 emits beta radiation (average energy greater than 10% probability: 194 KeV, 918 KeV), and gamma radiation (greater than 10% probability: 602 Kev, 722 KeV, 1.69 MeV), and has a half life of 60 days. What detection equipment and PPE would you use for entry activities? 6. Based on the US EPA definition of contamination, your department’s SOG states that victims and personnel will be considered decontaminated at a level below two times normal background. For this scenario, the normal background radiation level around Encinal, TX is 25 µR/hr or 15 CPM on a detector calibrated to Cs-137. What level of contamination would require decontamination? A. 51 µR/hr B. 50 µR/hr C. 30 CPM D. 1000 CPM |